The
Afro-Asiatic Family
of Languages






¡@
¡@
The Afro-Asiatic Family is dominated by Arabic, an important modern and classical language. It is the language of the Quran and of Islam. It is spoken in many Middle East and North African countries and studied outside that region. There are many regional variations and accents.
¡@

¡@

Many important ancient languages belong to this branch. Akkadian (the language of the Assyrian Empire) used the Cuniform writing system to write pre-Biblical flood and creation stories. Phoenician and its closely related relatives Ugaritic (for which the alphabet was invented) and Punic (the language of Carthage). Nabatean, an ancestor of Arabic spoken in Petra. Nearby were the languages of the Amorite and Moabite people.
Syriac, a liturgical language of the early Christian church. The most interesting is Aramaic, once the administrative language of the Perisan Empire, later the language of Palestine during Roman times. It now survives in small pockets in Syria, Iraq, Turkey and Iran where it is called Assyrian.
¡@
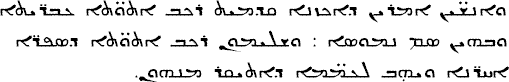
People in Ethiopia, Eritrea, Sudan and Somalia speak languages of the Cushitic Branch (Somali, Galla, Beja, Afar).
Hausa, the most important member of the Chadic Branch, is the main language of Nigeria. It was once written in the Arabic script but now uses the Latin alphabet. The Chadic Branch contains 600 languages spoken in Nigeria, Chad and Cameroon.
The Egyptian Branch contains Egyptian the language of Ancient Egypt written in hieroglyphics. Coptic, is the liturgical language of the Egyptian Coptic Church. It uses a Greek based alphabet. It is extinct as a spoken language.
¡@

For example, Arabic uses clusters of three consonants, called roots. For example, in Arabic, the triplet root K-T-B has to do with writing. KiTaB is book. Plurals are all irregularly formed and the usual way is to change the vowels. KuTuB is books. Other words with the KTB root have something to do with writing: KaTaBa - to write, KaTtaBa - to make someone to write (ie to teach), maKTaB - office, KaaTiB - writer, maKTaBa - library, miKTaB - typewriter, KuTuBii - bookseller, maKTuuB - fate ("that which is written"). The consonant root gives the core meaning while the vowels, suffixes and prefixes give the grammatical meaning.
An interesting example in Hebrew is the tripple root SH-B-T, which has to do with resting. One of its forms is the third person past tense of the verb, SHaBaT (he rested) which denotes the sabath on which the deity rested.
The Arabic alphabet mainly uses consonants because the reader can supply the correct vowels from the context. The first Alphabets were invented by speakers of Semitic languages and so had no vowels.
Unusually for this family, Somali has 20 separate vowel sounds. It also has four tones which indicate gender, number and case.
This language family originated in the Sahara area before it became a desert and spread to the Horn of Africa, North Africa and the Middle East. During the 7th Century AD, Arabic spread from the Arabian Peninsula with Islam to cover most of North Africa and the Middle East.
¡@
¡@
| Semitic Branch |
|---|
| Arabic : Maltese : Hebrew : Amharic : Tigrinya : Tigre Aramaic : Gurage : Harari : Geez Syriac : Akkadian : Phoenician : Punic : Ugaritic Nabatean : Amorite : Moabite |
| Berber Branch |
| Shluh : Tamazight : Riffian : Kabyle : Shawia : Tuareg Guanch |
| Cushitic Branch |
| Somali : Galla : Sidamo : Beja : Afar : Saho |
| Egyptian Branch |
| Egyptian : Coptic |
| Chadic Branch |
| Hausa |