2.活動的構音器官Moveable articulators
包括舌頭、唇、咽、下頷骨和軟顎。
They are tongue, lips, pharynx, mandible, and velum.
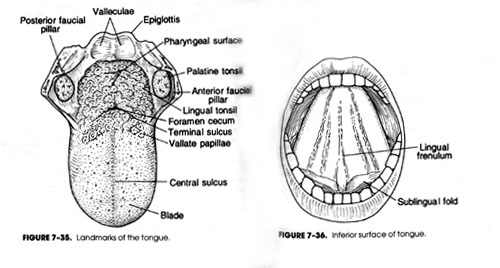
2.1 舌(tongue)
舌是味覺的主要感官感受,在語言方面也扮演了重要的角色,此外還參與了咀嚼及吞嚥的生理活動。其位於口腔底部,下頷的內側。
(1)舌根(lingual root)
(2)舌尖(lingual apex)
(3)舌腹(lingual undersurface)
(4)舌背(lingual dorsum)
(5)舌乳頭(lingual papillae)—輪狀乳頭(papillae vallate);絲狀乳頭(papillae filiforms);蕈狀乳頭(fungiforms);葉狀乳頭(papillae foliate)
(6)舌的肌肉—舌中隔(median septum)將舌分割為兩半,每半有兩組肌肉。起源於舌外的稱外源肌,其他為內源肌。
(7)神經支配—舌神經(lingual nerve)鼓索神經(chorda tympani nerve)舌咽神經的舌枝(glossopharyngeal nerve)喉上神經(superior laryngeal nerve)
(8)血管分佈
(9)淋巴引流
The superior surface is referred to as the dorsum, and the anterior-most portion is the tip or apex. The base of the tongue is the portion of the tongue that resides in the oropharynx. The portion of the tongue surface within the oral cavity is referred to as the oral or palatine surface, making up two thirds of the surface of the tongue. The other one third of the tongue surface lies within the oropharynx and is referred to as the pharyngeal surface.

圖片摘自Seikel, et al. Anatomy and Physiology for Speech, Language, and Hearing
咽腔位於鼻腔口腔後面,也是呼吸道及消化道為一相互交叉的地方,人體營養必須經此輸入,我國自古所謂咽喉要道,可知其重要性。
(1)鼻咽(nasopharynx),也稱為上咽(epipharynx)
(2)口咽(oropharynx),也稱中咽(mesopharynx)
(3)喉咽(laryngopharynx),也叫下咽(hypopharynx)
(4)咽壁—黏膜;咽腱膜;咽的肌肉(pharyngeal muscles)
(5)咽部神經支配
(6)血管分佈
(7)咽部淋巴組織
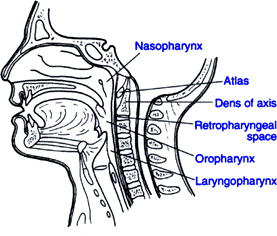
圖片摘自 http://ha.mtroyal.ab.ca/figs/l31/310100.htm (此網站有更詳細的解剖圖)
The pharynx is the part of the vocal tract that connects the larynx and the esophagus with the mouth and the nose. At its lower end, the pharynx meets the larynx and the esophagus; at its wider upper end, it joins with the back of the mouth and the nose. Its shape and size are changed when swallowing, either by moving the tongue back, or the larynx up, or by contracting the pharyngeal walls.
以上摘自Anatomy and Physiology for Speech, Language, and Hearing. (written by John A. Seikel, Douglas W. King, and David G. Drumright)